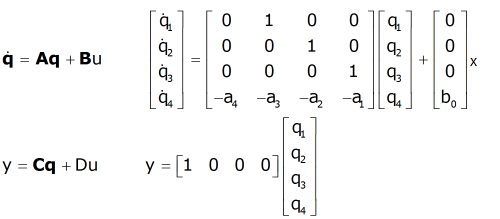In physics, the state of a system refers to a complete description of all the physical properties that are relevant to the behavior of that system. The state of a system can include a wide range of parameters, such as the position and momentum of every particle in the system, the energy and temperature of the system, and the magnetic field or other external forces acting on the system.
The state of a system is important because it determines how the system will evolve over time, according to the laws of physics. For example, the state of a gas in a container determines how it will expand or contract in response to changes in temperature or pressure.
In quantum mechanics, the state of a system is described by a wave function, which provides a complete mathematical description of the system’s properties. The wave function contains information about the position, momentum, and other physical properties of the particles in the system, and can be used to predict the probability of observing different outcomes in measurements of those properties.
The state of a system is a fundamental concept in physics, and is crucial to understanding the behavior of physical systems at all scales, from the smallest particles to the largest structures in the universe.