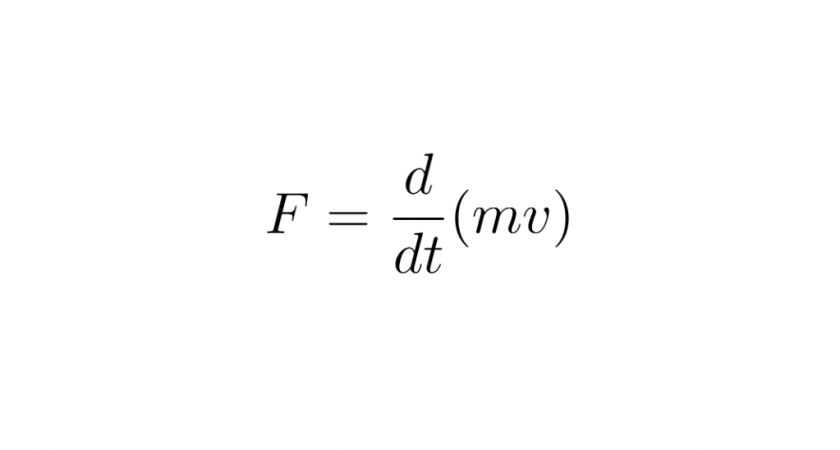The second law of motion in differential form.
This equation is known as the equation of motion, or the second law of motion in differential form. It is a differential equation that describes the relationship between the net force acting on an object and its momentum, which is the product of its mass and velocity.
This equation is more accurate than its antiderivative F=ma, when mass is not constant.